In this article
Help us make these docs great!
All rapyuta.io docs are open source. See something that's wrong or unclear? Submit a pull request.
Make a contributionDevice Routed Network for Local Communication
Complex robotic applications involving multi-device communication can be latent when the service is distributed across WAN. This tutorial demonstrates how to have multi-device communication within the same LAN.
Learning objectives
This tutorial will show you how to deploy a device routed network locally for inter-device communication using rapyuta.io console.
Prerequisites
- Device requirements
- You should have access to three devices (computer or Raspberry PI 2 or 3) with an internet connection.
- Install the latest Google Chrome browser on the device.
- Ensure the ROS Melodic Morenia is installed on the device.
- You should be familiar with the following tools:
- ROS topics
- UNIX/LINUX command terminal
Estimated time
20 minutes
Tutorial walkthrough
In this tutorial, you will add three devices namely _device_rn, Publisher Device and Subscriber Device. You will also create and deploy ROS Publisher and ROS Subscriber packages.
Add a Device
Ensure that the device must be of amd64 CPU architecture.
- Click Devices>All Devices > ADD NEW DEVICE.
- In the Device Name box, enter the name of the device, for example,
device_rn - Use docker compose as the default runtime option.
- Ensure the ROS Version is Melodic.
- In the Description box, provide a summary of the device, for example,
I am a Device Routed Network - Click CONTINUE.
- Click COPY to copy the generated Token.
Paste and execute the token in the device’s terminal to set up the rapyuta.io client on the device.
If the device is set up successfully, you should see the following output at the device’s terminal:
Initializing the Rapyuta Platform
############(100%)
Successfully Installed!
Ensure that there’s a green dot next to the Publisher Device, which indicates that it is online on rapyuta.io.
Prepare Publisher Device
The Publisher Device is:
- Raspberry PI 2 or 3
- can have either arm64v8 or arm32v7 CPU architecture
- must have ROS Melodic installed on it
- must have rapyuta.io tutorials installed on it
The custom rapyuta.io image comes with Ubuntu Xenial OS and ROS Melodic Moreniasoftware installed on them. Moreover, the rapyuta.io tutorials are also installed on these custom images.
Learn how to prepare Raspberry PI
If you are using a custom rapyuta.io image on the device, the catkin workspace is already set up for you, the io_tutorials repository is already downloaded in the workspace, and the source code is already built for you.
In this tutorial, the catkin workspace is ~/catkin_ws/, but you
may choose to name your catkin workspace as you like and ensure
that you replace all occurrences to ~/catkin_ws/ with your
workspace name.
If you are using either a computer with ROS Melodic installed on it, or a Raspberry PI without custom rapyuta.io image, you will create a catkin workspace and get the io_tutorials repository into the workspace.
To create the catkin workspace, you have to execute the below commands at the device’s terminal.
cd $HOME
mkdir -p catkin_ws/src
cd catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/rapyuta/io_tutorials
source /opt/ros/melodic/setup.bash
cd ..
For the custom rapyuta.io image to support the build command, catkin build, you will set up the device by executing the following:
cd $HOME &&
mv catkin_ws catkin_old &&
curl https://storage.googleapis.com/artifacts.rapyuta.io/io_tutorials/catkin_ws_arm32v7.tar.gz | tar xz
The argument to the curl command, i.e., the URL address, changes based on the architecture of the device.
- For a device with an arm64 architecture, use https://storage.googleapis.com/artifacts.rapyuta.io/io_tutorials/catkin_ws_arm64v8.tar.gz
- For a device with an arm32 architecture, use https://storage.googleapis.com/artifacts.rapyuta.io/io_tutorials/catkin_ws_arm32v7.tar.gz
- For a device with an amd64 architecture, use https://storage.googleapis.com/artifacts.rapyuta.io/io_tutorials/catkin_ws_amd64.tar.gz
To build the source code in the catkin workspace, execute the below command in the root of the workspace:
catkin build talker
If you experience the error catkin:command not found, then the python-catkin-tools package is missing on the device, which is required for executing catkin build command. Install the package by running the command sudo apt-get install python-catkin-tools at the device terminal.
Add Publisher Device
- Click Devices>All Devices > ADD NEW DEVICE.
- In the Device Name box, enter the name of the device, for example,
Publisher Device - In the ROS Catkin Workspace box, enter the absolute path of the catkin workspace found on the device.
If rapyuta.io custom image is installed on the device, the absolute path of the catkin workspace is
/home/rapyuta/catkin_ws.
Otherwise, the absolute path of the catkin workspace will be different for the device. - In the Description box, provide a summary of the device, for example,
I am a ROS Publisher - Click CONTINUE.
- Click COPY to copy the generated Token.
Paste and execute the token in the device’s terminal to set up the rapyuta.io client on the device.
If the device is set up successfully, you should see the following output at the device’s terminal:
Initializing the Rapyuta Platform
############(100%)
Successfully Installed!
Ensure that there’s a green dot next to the Publisher Device, which indicates that it is online on rapyuta.io.
Prepare Subscriber Device
The Subscriber Device is a:
- Raspberry PI 2 or 3
- can have either arm64v8 or arm32v7 CPU architecture
- must have ROS Melodic installed on it
- must have rapyuta.io tutorials installed on it
The custom rapyuta.io image comes with Ubuntu Xenial OS and ROS Melodic Morenia software installed on them. Moreover, the rapyuta.io tutorials are also installed on these custom images.
Learn how to prepare Raspberry PI
If you are using a custom rapyuta.io image on the device, the catkin workspace is set up for you, the io_tutorials repository is downloaded in the workspace, and the source code is built for you.
In this tutorial, the catkin workspace is ~/catkin_ws/, but you
may choose to name your catkin workspace as you like and ensure
that you replace all occurrences to ~/catkin_ws/ with your
workspace name.
If you are using either a computer with ROS installed on it or a Raspberry PI without custom rapyuta.io image, you will create a catkin workspace and get the io_tutorials repository into the workspace.
To create the catkin workspace, you have to execute the below commands at the device’s terminal:
cd $HOME
mkdir -p catkin_ws/src
cd catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/rapyuta/io_tutorials
source /opt/ros/melodic/setup.bash
cd ..
For the custom rapyuta.io image to support the build command, catkin build, you will set up the device by executing the following:
cd $HOME &&
mv catkin_ws catkin_old &&
curl https://storage.googleapis.com/artifacts.rapyuta.io/io_tutorials/catkin_ws_arm32v7.tar.gz | tar xz
The argument to the curl command, i.e., the URL address, changes based on the architecture of the device.
- For a device with an arm64 architecture, use https://storage.googleapis.com/artifacts.rapyuta.io/io_tutorials/catkin_ws_arm64v8.tar.gz
- For a device with an arm32 architecture, use https://storage.googleapis.com/artifacts.rapyuta.io/io_tutorials/catkin_ws_arm32v7.tar.gz
- For a device with an amd64 architecture, use https://storage.googleapis.com/artifacts.rapyuta.io/io_tutorials/catkin_ws_amd64.tar.gz
To build the source code in the catkin workspace, execute the below command in the root of the workspace:
catkin build listener
If you experience the error catkin:command not found, then the python-catkin-tools package is missing on the device, which is required for executing catkin build command. Install the package by running the command sudo apt-get install python-catkin-tools at the device terminal.
Add Subscriber Device
- Click Devices>All Devices > ADD NEW DEVICE.
- In the Device Name box, enter the name of the device, for example,
Subscriber Device - In the ROS Catkin Workspace box, enter the absolute path of the catkin workspace found on the device.
If rapyuta.io custom image is installed on the device, the absolute path of the catkin workspace is/home/rapyuta/catkin_ws
Otherwise, the absolute path of the catkin workspace will be different for the device. - In the Description box, provide a summary of the device, for example,
I am a ROS Subscriber - Click CONTINUE.
- Click COPY to copy the generated Token.
Paste and execute the token in the device’s terminal to set up the device manager client on the device.
If the device is set up successfully, you should see the following output:
Initializing the Rapyuta Platform
############(100%)
Successfully Installed!
Ensure that there’s a green dot next to the Subscriber Device, which indicates that it is online on rapyuta.io.
Create ROS Publisher package
-
Click Development > Packages > ADD NEW PACKAGE.
-
You should provide information about the package such as the name of the package, its version, whether it is a singleton package, and a description.
- In the Package Name box, enter the name of the package, for example,
ROS Publisher - In the Package Version box, type in the package’s version. By default, the version is set to 1.0.0
- Ensure Is a singleton package checkbox is not selected.
- Ensure Is a bindable package checkbox is not selected.
- In the Description box, provide a summary of the package, for example,
Publishes ROS topic for a subscriber - Click NEXT.
- In the Package Name box, enter the name of the package, for example,
-
In the Component Name box, enter a name for the component, for example,
Publisher -
Select Device as the Component Runtime.
-
Ensure Is ROS Component is selected.
-
Ensure the ROS Version is Melodic.
-
In the Executable Name box, type in a name for the executable, for example,
talker -
For Executable type, select Default because the source code is already installed on the Publisher Device.
-
In the Command to run in the docker container box, copy and paste the command:
roslaunch talker talker.launchEnsure you always execute roslaunch command for explicitly starting the ROS Master instead of running the rosrun command, because the ROS Master will fail to start on rosrun, and eventually, the deployment will fail as well.
-
To add a ROS topic, click Add ROS topic. In the Name box, enter
/telemetryand set QoS to Maximum. -
Click NEXT > CONFIRM PACKAGE CREATION.
Create ROS Subscriber package
-
Click Development > Packages > ADD NEW PACKAGE.
-
You should provide information about the package such as the name of the package, its version, whether it is a singleton package, and a short description.
- In the Package Name box, enter the name of the package , for example,
ROS Subscriber - In the Package Version box, type in the package’s version. By default, the version is set to 1.0.0
- Ensure Is a singleton package checkbox is not selected.
- Ensure Is a bindable package checkbox is not selected.
- In the Description box, provide a summary of the package , for example,
Subscribes to ROS topic published by a publisher - Click NEXT.
- In the Package Name box, enter the name of the package , for example,
-
In the Component Name box, enter a name for the component, for example,
Subscriber -
Select Device as the Component Runtime.
-
Ensure Is ROS Component is selected.
-
Ensure the ROS Version is Melodic.
-
In the Executable Name box, type in a name for the executable, for example,
listener -
For Executable type, select Default because the source code is already installed on the Subcriber Device.
-
In the Command to run in the docker container box, copy and paste the command:
roslaunch listener listener.launchEnsure you always execute roslaunch command for explicitly starting the ROS Master instead of running the rosrun command, because the ROS Master will fail to start on rosrun, and eventually, the deployment will fail as well.
-
Click NEXT > CONFIRM PACKAGE CREATION.
Create a Device Routed Network
Follow these steps to create a device routed network. Make sure you have a rapyuta.io registered device with docker runtime.
- On the left navigation bar, click NETWORKS.
- Click ADD NETWORK. Select Routed network in the pop-up..
- Enter
device_routed_network_1as the name for the routed network. - Select ROS Distro as Melodic.
- Select the Runtime as Device.
- You will see a list of online device with docker runtime and AMD64 architecture in the drop-down list.
Select the Device as
Routed_Network_Deviceand its IP Interface. - Select the Restart policy.
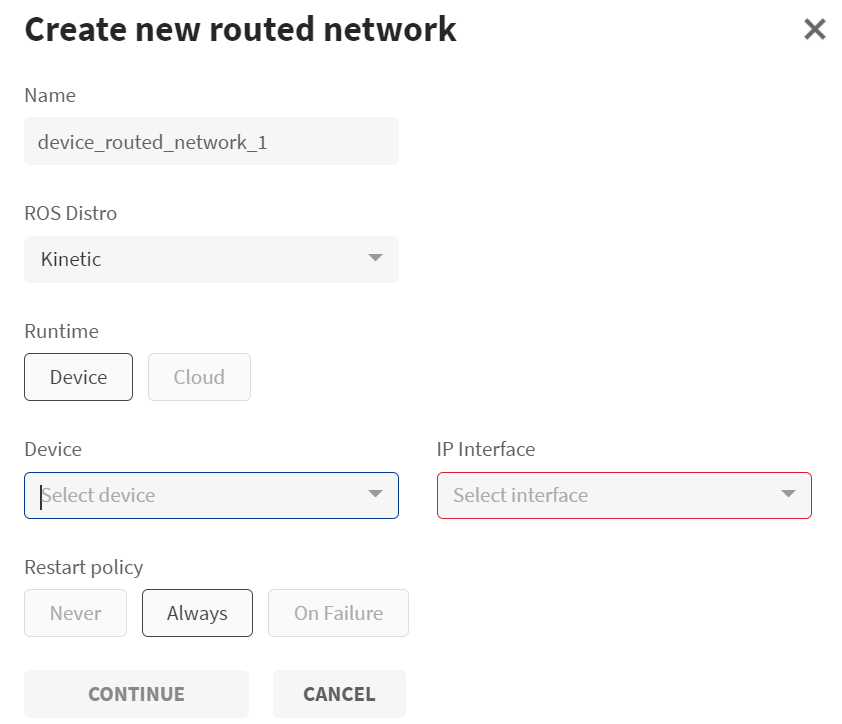
- Click CONTINUE.
The routed network is getting deployed and is identical to the deployment of any other package and has identical corresponding phases and errors. Once the routed network deployment succeeds, other ROS package deployments can bind to it and communicate.
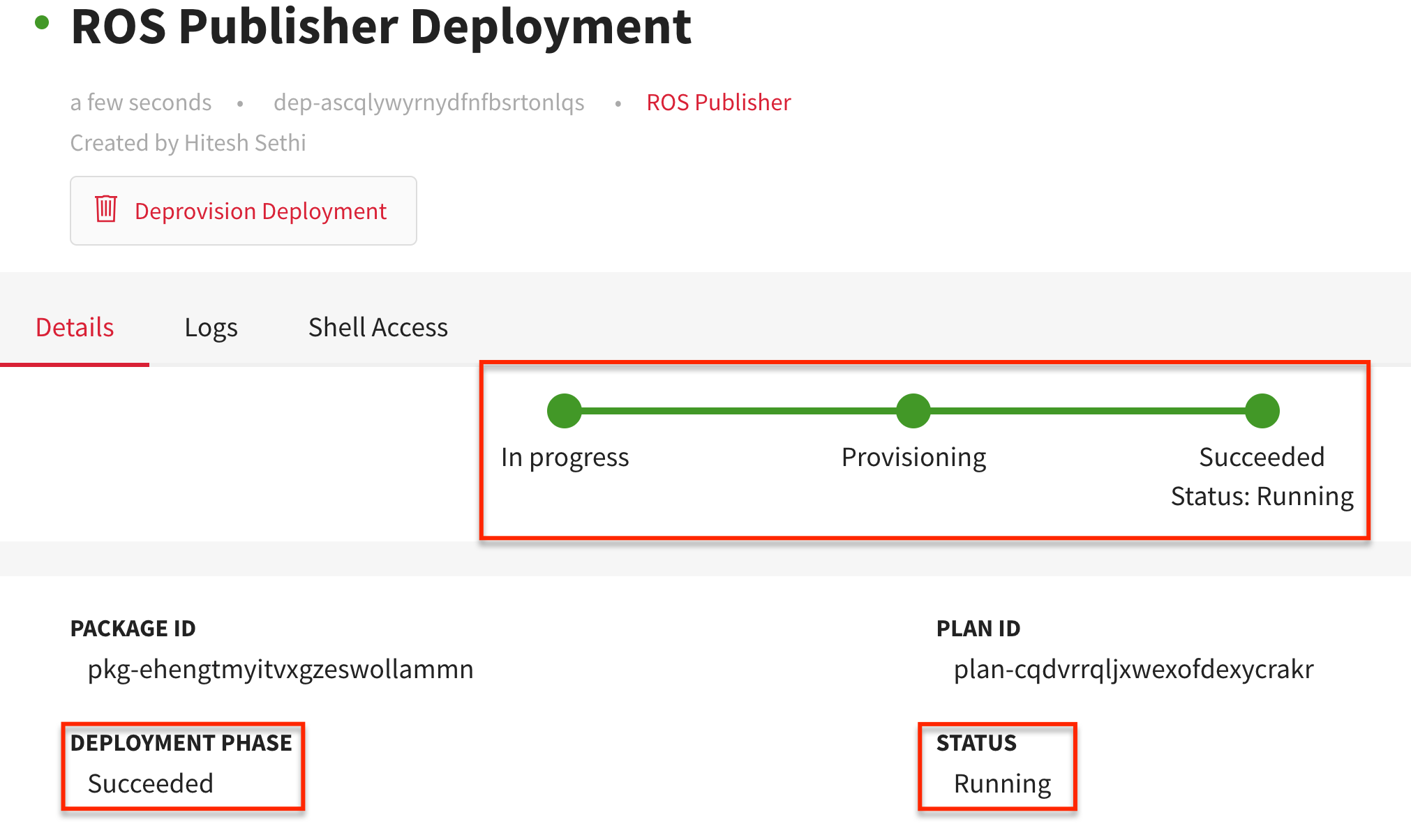
Deploy ROS Publisher package
- Click Development > Packages > select ROS Publisher package > click Deploy package.
- In the Name of deployment box, enter a name for the deployment
, for example,
ROS Publisher Deployment - Since Publisher has Device runtime, select the device you want to deploy on by clicking Refresh the list of online devices. It retrieves an updated list of online devices.
- Select Publisher Device from Select device for deploying the component drop-down list.
- Under Device Config Variables, ensure that the ros_workspace and ros_distro are selected.
- Click Add next to the Routed Network field.
- From the Network drop-down menu, select
device_routed_network_1as the device routed network. - Click CREATE DEPLOYMENT > Confirm.
You will be redirected to the Details tab of the newly created deployment. The package is successfully deployed when the green colored bar moves from In progress to Succeeded indicating that the DEPLOYMENT PHASE has Succeeded and the STATUS is Running.
You may analyze the corresponding deployment logs so you may debug if the deployment fails.
The corresponding dependency graph of ROS Publisher Deployment looks like:
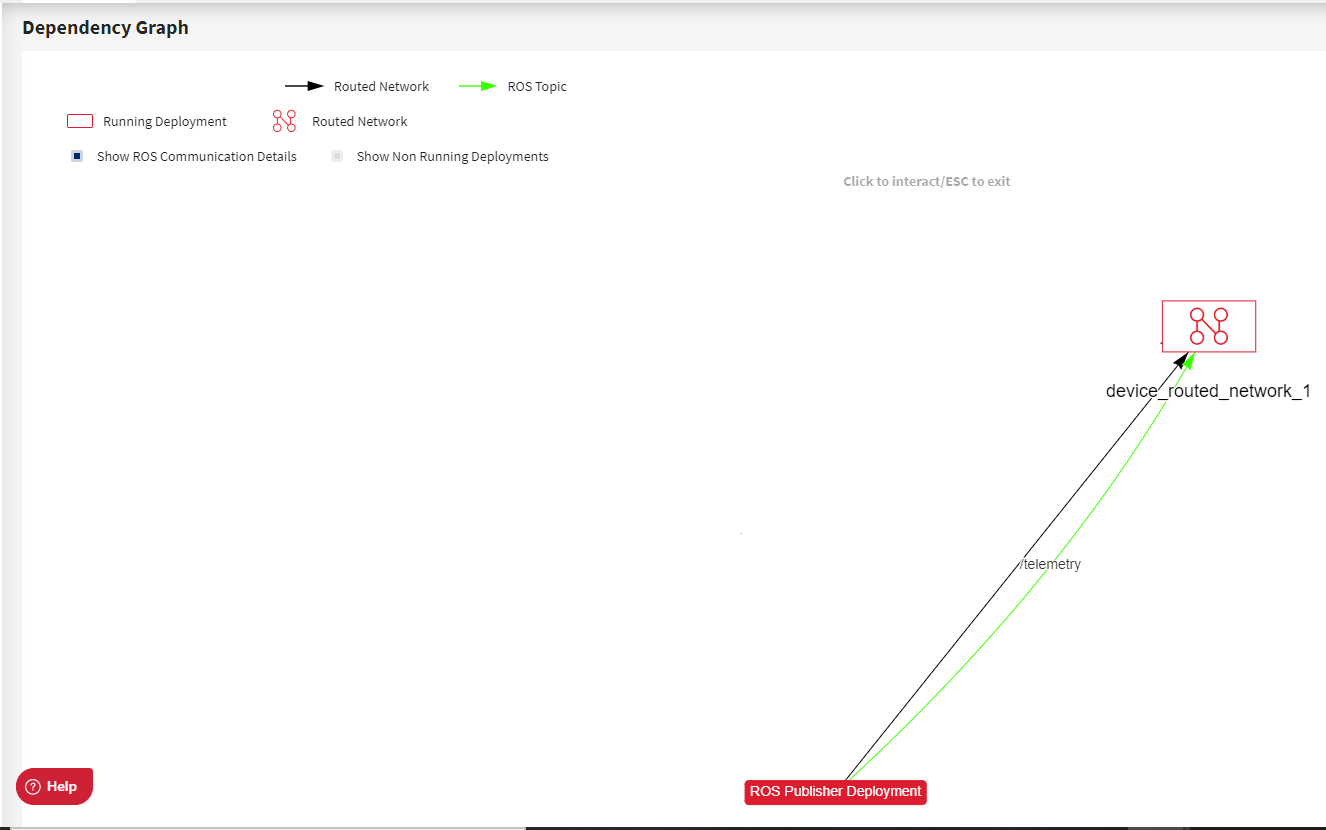
Deploy ROS Subscriber package
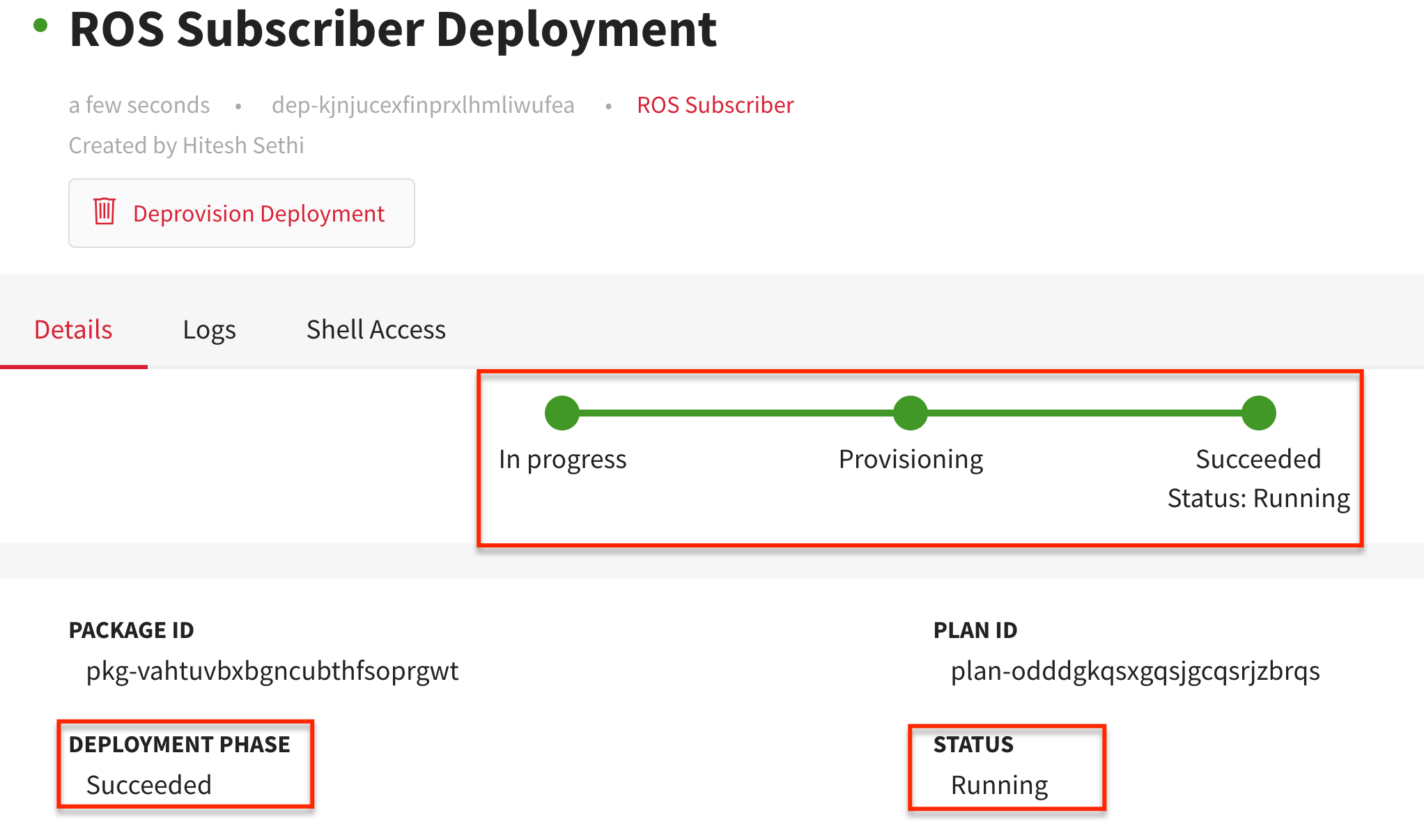
- Click Development>Catalog > select ROS Subscriber package > click Deploy package.
- In the Name of deployment box, enter a name for the deployment, for example,
ROS Subscriber Deployment - Since Subscriber has Device runtime, select the device you want to deploy on by clicking Refresh the list of online devices. This retrieves an updated list of online devices.
- Select Subscriber Device from the Select device for deploying the component drop-down list.
- Ensure that ros_workspace and ros_distro are selected.
- From the Network drop-down menu, select
device_routed_network_1as the device routed network. - Click CREATE DEPLOYMENT > Confirm.
You will be redirected to the newly created deployment’s Details tab. The package is successfully deployed when the green colored bar moves from In progress to Succeeded indicating that the DEPLOYMENT PHASE has Succeeded, and the STATUS is Running.
You may analyze the corresponding deployment logs so you may debug if the deployment fails.
The corresponding dependency graph of ROS Subscriber Deployment looks like:
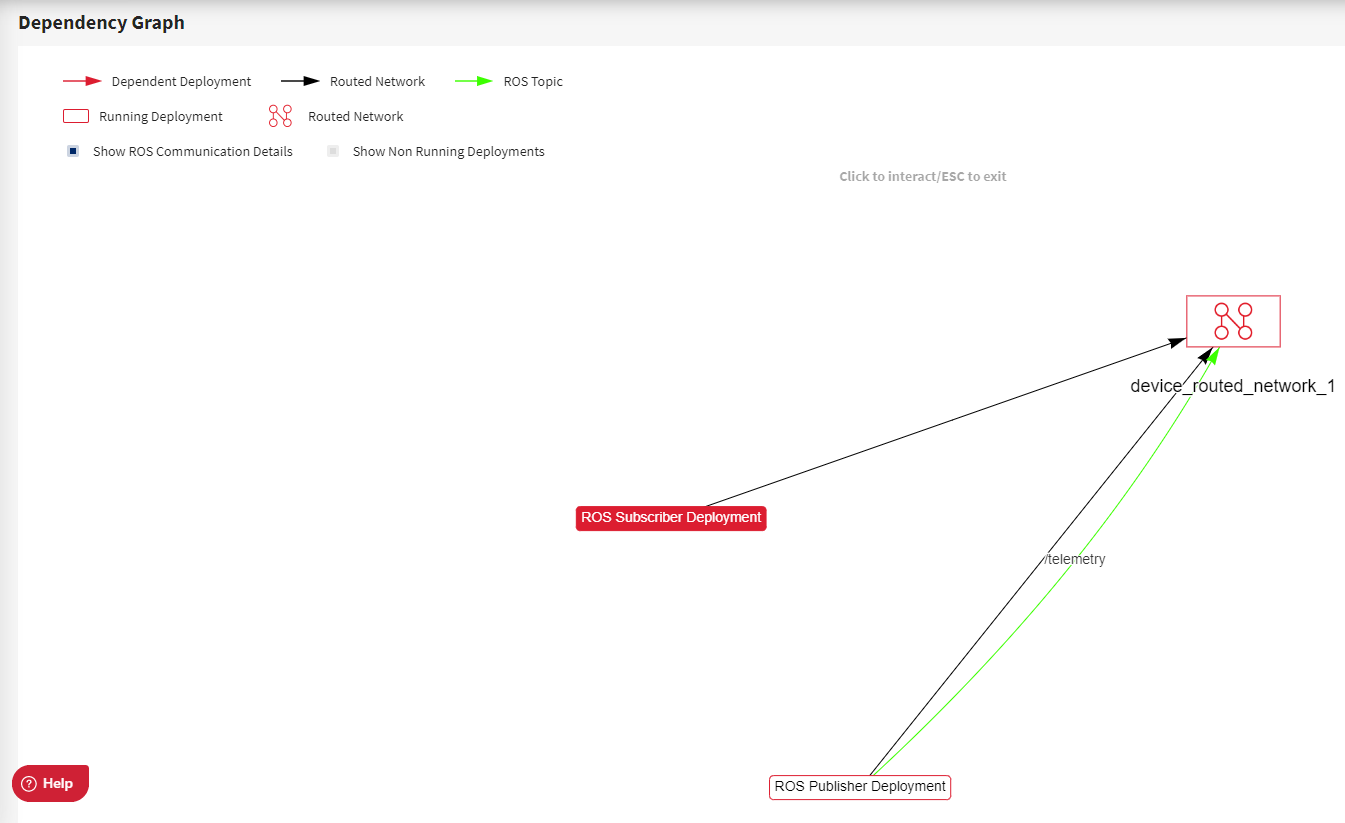
If all of the above three deployments are successfully running, the logs of ROS Subscriber Deployment will print hello_world.
Since the device routed network is deployed on the device_rn locally, and the bindable attribute is not selected (value is set to false) for both the ROS Publisher package and the ROS Subscriber package, the ROS topic (/telemetry) and in general, the data is transferred within the same local network. Thus, the application’s latency is comparatively reduced provided the device_rn is in the same network as the Publisher Device, and Subscriber Device.