In this article
Help us make these docs great!
All rapyuta.io docs are open source. See something that's wrong or unclear? Submit a pull request.
Make a contributionPython SDK : Publisher Subsciber
A ROS publisher is part of a ROS package. It is a public git repository, which is built into a running docker container on the fly when the package is being deployed. A ROS subscriber is also a part of the same ROS package. It is downloaded on a device and is launched when the package is deployed.
Learning objectives
The walkthrough gives an overview of how to:
- configure and provision a package
- create a routed network
- deploy a package on the cloud
- deploy a package on a device
programmatically using rapyuta.io Python SDK in your python application.
Prerequisites
- Read the rapyuta.io platform documentation
- Install rapyuta.io SDK in your development environment and obtain the following. For more information, click here
- authorization token
- project ID
- package ID
- plan ID
- device ID
Estimated time
25 minutes
Assumptions
- Talker is a ROS package created in rapyuta.io, and it behaves as a ROS publisher.
- Listener is another ROS package created in rapyuta.io, and it behaves as a ROS subscriber. LISTENER is the component of the package that will be deployed on a device.
- PROJECT_ID is a unique identification value of the project in which Talker and Listener packages are created. It is of type string.
- TALKER_ID and LISTENER_ID are the package IDs of the Talker and Listener packages respectively. The values are of type string.
- TALKER_PLAN_ID and LISTENER_PLAN_ID are the plan IDs of the default plan of Talker and Listener packages, respectively. The values are of type string.
- AUTH_TOKEN is the authorization token for accessing rapyuta.io resources and services. Its value is of type string.
- DEVICE ID is a unique identification value of a device on rapyuta.io, and it is of type string.
Creating the io-tutorial build
To create the build, follow the below steps. Skip the following steps if you have already created an io-tutorials build earlier.
- On the left navigation bar, click Development>Builds.
- Click on ADD NEW BUILD
- In the Build Name box, enter a name for the build, for example,
io-tutorials - In the Git repository box, enter the URL address:
https://github.com/rapyuta/io_tutorialsand select Build Recipe as Catkin. - Go to the next step and click on next, the build will be created.
The build takes about two to five minutes to build the source code in the io_tutorials repository into a running docker container. You may analyze the corresponding build logs, which helps in debugging failed builds. After you create the build, create the Talker and Listener package.
Create Talker Package
- On the left navigation bar, click Development > Packages.
- Click ADD PACKAGE.
- In the Package Name box, type in a name for the package like
Talker. - In the Package Verison box, enter the version of the package you are creating. The default value is 1.0.0
- Make sure Is singleton package is not selected.
- Ensure Is bindable package is selected.
- In the Description box, explain what the package is about,
for instance, the description of this package is
ROS Publisher. - Click NEXT.
- In the Component Name box, enter a name for the component, for example,
TALKER. - Select Cloud for Component Runtime.
- Ensure Is ROS Component is selected.
- Select Melodic for ROS Version.
- The default value of Replicas to run the component is set to 1
- In the Executable Name box, enter a name for an executable, for example,
talker_executable. - Click Development>Builds for Executable Type.
- Select io-tutorials builds from the dropdown
- In the Command to run in the docker container box, enter the command:
roslaunch talker talker.launch - The talker_executable publishes a ROS topic
/telemetry. To add a ROS topic, click Add ROS topic. In the Name box, type in the ROS topic. Select Maximum as the value for QoS. - Click NEXT > CONFIRM PACKAGE CREATION.
Create Listener Package
- On the left navigation bar, click Development>Catalog.
- Click ADD PACKAGE.
- In the Package Name box, type in a name for the package
like
Listener. - In the Package Version box, enter the version of the package you are creating. The default value is 1.0.0
- Make sure Is singleton package is not selected.
- Ensure Is bindable package is selected.
- In the Description box, explain what the package is about,
for instance, the description of this package is
ROS Subscriber. - Click NEXT.
- In the Component Name box, enter a name for the component, for example,
LISTENER. - Select Device for Component Runtime.
- Ensure Is ROS Component is selected.
- Select Melodic for ROS Version.
- Set Restart Policy to Never.
- In the Executable Name box, enter a name for an
executable , for example,
listener_executable. - Set Executable Type to Default.
- In the Command to run in the docker container box, enter
the command:
roslaunch listener listener.launch - Click NEXT > CONFIRM PACKAGE CREATION.
Create Cloud Routed Network
A routed network allows you to establish ROS communication between different ROS package deployments. Binding a routed network resource to your deployment will enable other deployments on the same routed network to consume ROS topics/services/actions as defined in the package. If you have already created a routed network, you can skip this procedure.
Use the following code to create a routed network
routed_network = client.create_cloud_routed_network("CLOUD_ROUTED_NETWORK", ROSDistro.MELODIC, True)
routed_network.poll_routed_network_till_ready()
Code Walkthrough
Firstly, you need to authenticate to access rapyuta.io services from within your python application.
# Authentication
from rapyuta_io import Client
from rapyuta_io.clients.package import ROSDistro
client = Client(AUTH_TOKEN, PROJECT_ID)
# Create a Routed Network
routed_network = client.create_cloud_routed_network("CLOUD_ROUTED_NETWORK", ROSDistro.MELODIC, True)
routed_network.poll_routed_network_till_ready()
Retrieve the Talker package by its package ID, and then deploy it on the cloud. The resulting deployment is called ROS PUBLISHER.
# Deploy Talker package on cloud
talker = client.get_package(TALKER_ID)
talker_configuration = talker.get_provision_configuration(TALKER_PLAN_ID)
talker_configuration.add_routed_network(routed_network)
talker_cloud_deployment = talker.provision(deployment_name="ROS PUBLISHER", provision_configuration=talker_configuration)
talker_cloud_deployment.poll_deployment_till_ready()
Similarly, deploy Listener package on the cloud. Since the resulting ROS SUBSCRIBER deployment depends on ROS PUBLISHER deployment, add the latter as a dependent deployment of the former.
# Deploy Listener package on device
listener = client.get_package(LISTENER_ID)
listener_configuration = listener.get_provision_configuration(LISTENER_PLAN_ID)
device = client.get_device(DEVICE_ID)
listener_configuration.add_device("LISTENER", device)
listener_configuration.add_routed_network(routed_network)
listener_device_deployment = listener.provision(deployment_name="ROS SUBSCRIBER", provision_configuration=listener_configuration)
listener_device_deployment.poll_deployment_till_ready()
Put the above code snippets together in a file, talker-listener.py, save the program and close the file.
# talker-listener.py
from rapyuta_io import Client
# Authentication
client = Client(AUTH_TOKEN, PROJECT_ID)
# Create a Routed Network
routed_network = client.create_cloud_routed_network("CLOUD_ROUTED_NETWORK", ROSDistro.MELODIC, True)
routed_network.poll_routed_network_till_ready()
# Deploy Talker on cloud
talker = client.get_package(TALKER_ID)
talker_configuration = talker.get_provision_configuration(TALKER_PLAN_ID)
talker_configuration.add_routed_network(routed_network)
talker_cloud_deployment = talker.provision(deployment_name="ROS PUBLISHER", provision_configuration=talker_configuration)
talker_cloud_deployment.poll_deployment_till_ready()
# Deploy Listener on device
listener = client.get_package(LISTENER_ID)
listener_configuration = listener.get_provision_configuration(LISTENER_PLAN_ID)
device = client.get_device(DEVICE_ID)
listener_configuration.add_device("LISTENER", device)
listener_configuration.add_routed_network(routed_network)
listener_device_deployment = listener.provision(deployment_name="ROS SUBSCRIBER", provision_configuration=listener_configuration)
listener_device_deployment.poll_deployment_till_ready()
# Get status of ROS SUBSCRIBER deployment
print subscriber_deployment.get_status()
At the terminal prompt, run the program using the command:
$ python talker-listener.py
The output is an object of the class DeploymentStatus, which contains values such as:
- deployment ID
- deployment name
- deployment status
- deployment phase
- package ID and other details.
The final deployment is running successfully if the value of the deployment status is Running.
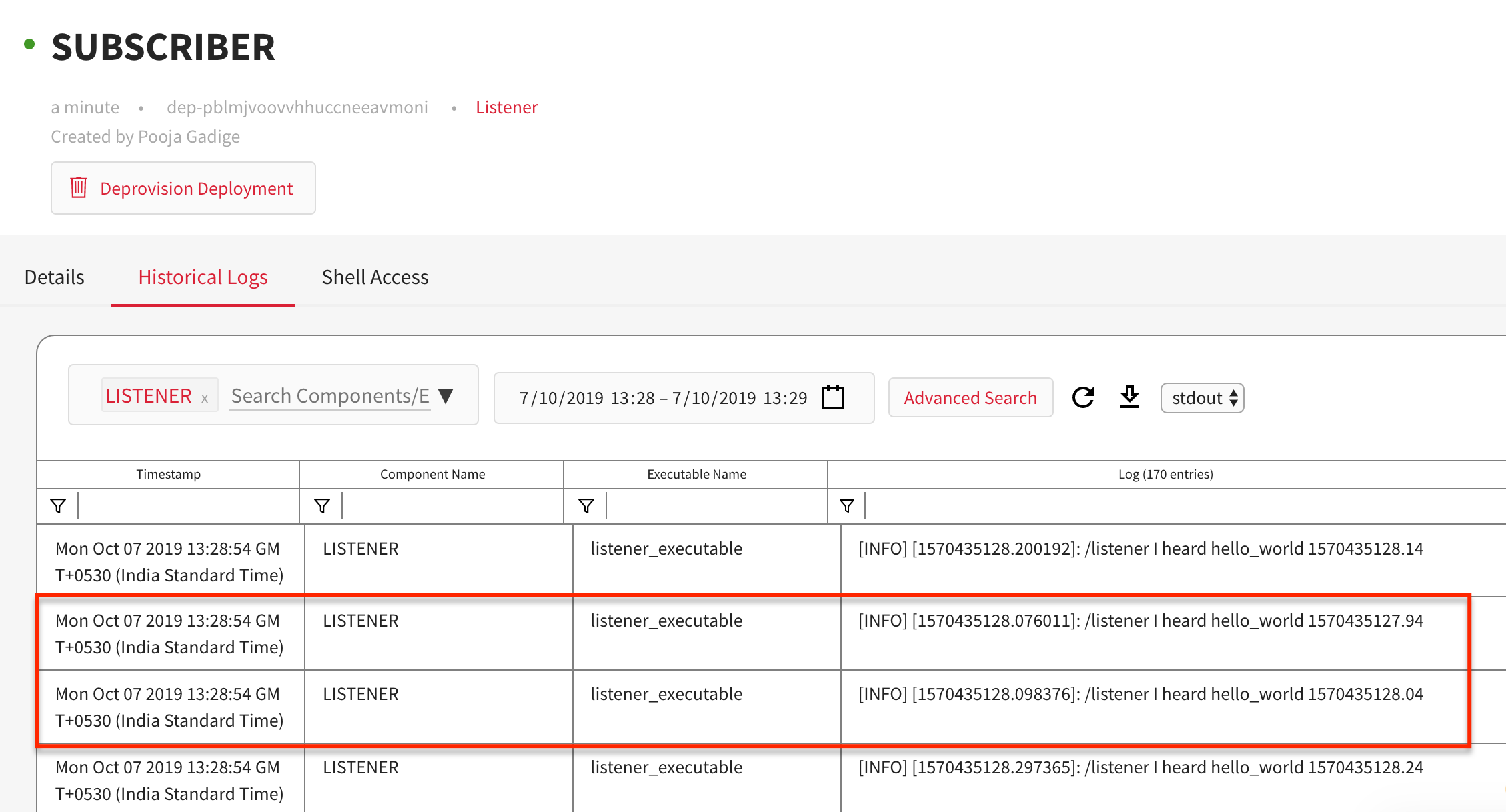
To verify if the program has executed correctly, click on the Historical Logs
tab of ROS SUBSCRIBER deployment to view the output as shown: